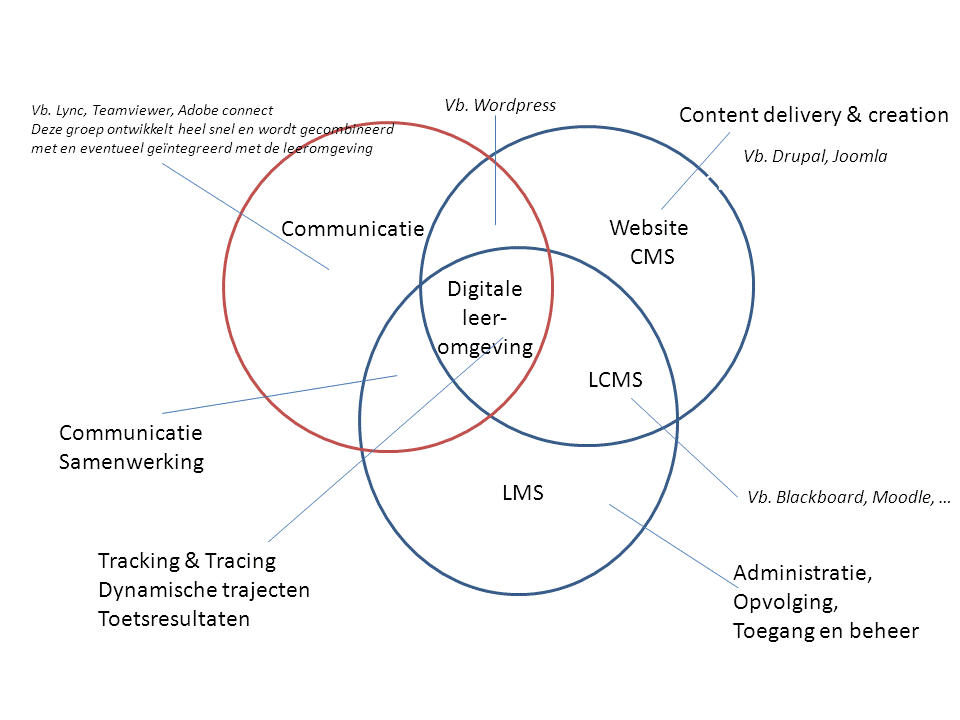
Definition
By a digital, or even electronic learning environment, we mean a learning platform designed to provide for educational content and to allow for the organization of learning paths, thus a platform to offer learning materials to the student.
It also performs several functions:
- communication between your students and/or the e-coach
- access to the e-content (administrator, rights, management …)
- tracking the learning process (progress, test results, counseling, …)
The figure below shows the intersection of these three points and is described as a fully fledged digital learning environment.